PC gaming has always been about customisability, allowing you to change your game’s settings based on your hardware to walk the fine line between resolution and frame rate. Nvidia’s deep learning super sampling (DLSS) is a video rendering technique that’s designed to help you boost fps without sacrificing too much of your visual quality.
DLSS works by rendering the game at a lower resolution to reduce the stress placed on your GPU, before rebuilding the image back up to your chosen native resolution through artificial intelligence (AI). There are only two catches to the feature: it isn’t supported by every game, and, unlike AMD’s new FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR) and other forms of anti-aliasing, it’s a hardware solution that requires an RTX graphics card in order to run.
While Nvidia Reflex goes a long way to give you the competitive edge in FPS games, DLSS is debatably the most innovative feature Nvidia has released in recent years. It was originally created to make ray tracing more accessible by reducing the performance hit that comes with it, but has since crafted its own identity as of DLSS 2.0, independently appearing in games.
As of September, 2020, we are currently on DLSS 2.1, although you might still see people colloquially referring to the current iteration as DLSS 2.0. This is because the second generation provided a huge leap from the original, addressing artifacting issues that distorted visuals, removing peculiar limitations, and introducing three modes to choose from, while 2.1 is a smaller update that introduces a fourth option.
What is the best DLSS mode?
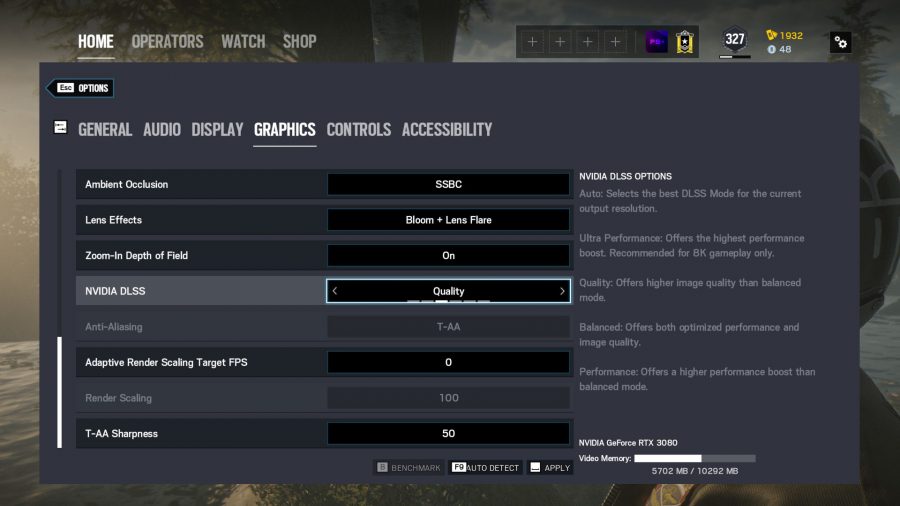
Currently, there are four DLSS modes to choose from: Quality, Balanced, Performance, and Ultra Performance. These mostly do what they say on the tin, either prioritising detail or putting greater emphasis on the frame rate. Looking at them from a technical standpoint, they refer to the relationship between the rendered image and the upscaled version:
Nvidia DLSS Quality mode
Provides a small fps boost and has the least impact on image quality.
With the render resolution of this preset being closer to the native resolution than other DLSS modes, it’s the most demanding of the bunch and offers the smallest performance improvement, but has the least impact on the overall quality.
This is recommended if you’re running the best gaming PC but want to squeeze more frames without sacrificing your game’s detail, particularly if you’re using the best gaming monitor with a 4K resolution. This is also the a good mode to try if other presets noticeably blur your game, as it’s sharper than the rest.
Nvidia DLSS Balanced mode
Has a respectable fps boost with a slight impact on quality.
You can think of Balanced as the average or ‘normal’ setting that acts as the middle-ground. It’s not quite as demanding as Quality, but it also doesn’t make the same visual sacrifices as Performance.
By its very nature, Balanced suits almost everyone, sticking as close to your chosen frame rate as possible. 4K users will benefit the most, though, as DLSS generally works better with more pixels involved.
Nvidia DLSS Performance mode
Offers the biggest fps boost, but carries more chance of blurring.
Nvidia often uses its Performance setting when showcasing just how many frames a DLSS-enabled game can push. It has a wider super sampling range to cover than Balanced or Quality, which offers a higher frame rate but sometimes comes with a hit to its visuals, including a loss in fidelity.
Performance mode is best for 1440p gamers, but it also comes in handy if you’re using a slower, aging system and want to get the most out of it.
Nvidia DLSS Ultra Performance mode
Gives the biggest frame rate jump, if you don’t mind blurry visuals.
Joining the roster a little later than the other options, this mode offers the lowest resolution rendering image compared to the chosen native resolution. As a result, you get the biggest leap in frame rate but this often comes with a noticeable hit to the visual quality.
This setting is geared more towards 8K users – not that many configurations can push such a high pixel count – but it also suits those wanting more frames at 4K by rendering at 720p instead of 1080p.
How good is DLSS Performance?
DLSS performance varies depending on hardware configurations, the game you’re playing, and whether or not you’re running ray tracing, making it difficult to put a number on exactly what you can expect. It’s also something that will get better over time through machine learning as the neural network improves, meaning we’ll likely see these margins increase.
Let’s take a look at some of Nvidia’s internal numbers to get an idea of what to expect (take these with a pinch of salt):

DOOM
DLSS makes ray tracing significantly more accessible, even when playing Doom Eternal at 4K resolution using max settings. Nvidia says DLSS accelerates frame rate by up to 60%, with nearly all RTX graphics cards reaching above 60fps.

Red Dead Redemption 2
Open world games are often a little more demanding than others, but Nvidia says any RTX graphics card can run Red Dead Redemption 2 at Full HD, above 60fps, on max settings with DLSS. It even lowers the barrier to entry at 4K resolution, boosting performance by up to 45%. Better yet, this extends to Red Dead Online, too.

Rainbow Six Siege
DLSS is particularly handy in competitive shooters, where each and every frame can mean the difference between a win and a loss. Quality mode is probably better if you’re running Rainbow Six Siege at 1080p or 1440p, but DLSS Performance mode lets you run 4K resolution without lowering your frame rate. You’ll see up to a 50% fps boost when running the game in UHD at max settings, and it even pushes the RTX 2060 into triple digits.

LEGO Builder’s Journey
Some would consider Lego Builder’s Journey nearly unplayable at 4K resolution using max settings, as even the best graphics cards fail to achieve more than 20fps – unless you use DLSS. 60fps is still unachievable with these settings, but a potential 163% increase in frame rate gets close enough on the RTX 3080 Ti, while other GPUs firmly sit above 30fps. Those of you that prioritise frame rate will want to crank things down to 1080p with DLSS Quality on instead.
Remember, these are Nvidia’s internal figures and you should take them with a pinch of salt. It goes to show how DLSS can also compensate for questionable optimisation, however, as well as facilitate a smoother experience on polished games.
How does DLSS work?
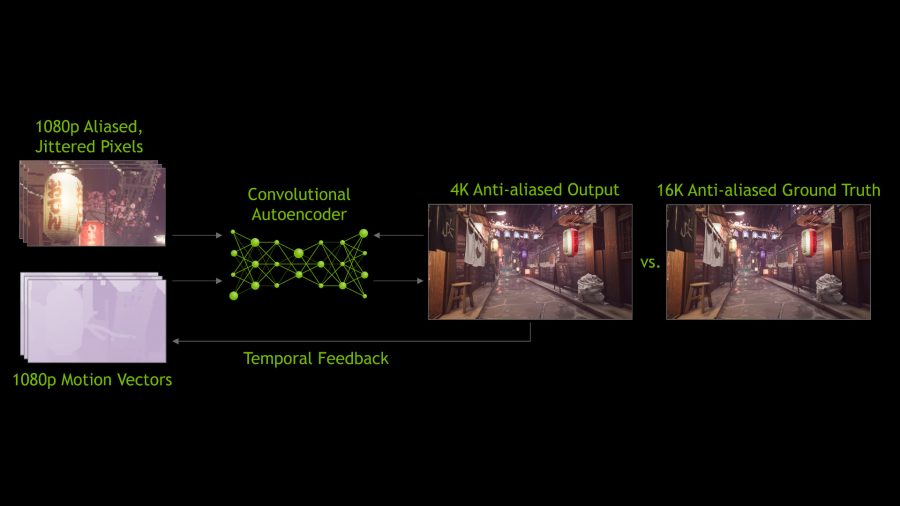
You may have heard the term ‘upscaling’ before, which goes some way towards visualising DLSS’s magic in action, but it’s a tad more complicated.
It all starts with the NGX supercomputer, where Nvidia trains its AI using machine learning. It feeds the neural network thousands of images, allowing the AI to compare ultra high resolution stills, that are presumably 64x super sampling anti-aliased versions, with lower resolution source images that haven’t been tampered with. This allows it to reference the quality of the source image and chart a path to rebuild it into the larger version using inference.
DLSS will vary from game to game – and even GPU to GPU – but Nvidia claims it “avoids the issues associated with TAA, such as screen-wide blurring, motion-based blur, ghosting and artifacting on transparencies.” This is partly thanks to its own temporal feedback techniques, which use motion vectors to calculate the movement of on-screen objects in advance, keeping DLSS one step ahead.
The first generation of DLSS required the AI to train for each and every game. DLSS 2.0, however, uses a general approach that allows the feature to learn over and apply AI enhancements automatically to all compatible games through Game Ready drivers. From there, RTX graphics cards use their Tensor Cores to push the improvements in real-time.
What graphics cards support DLSS?
Nvidia’s RTX 2000 and 3000 series of graphics cards are kitted out with Tensor Cores that enable DLSS, so it’s as easy as looking for the ‘RTX’ prefix to know whether your GPU will work with the feature. Unfortunately, DLSS isn’t available on AMD graphics cards because of this hardware requirement, but don’t despair if you’re rocking a Radeon GPU, as AMD’s FSR seems like a great open source alternative.
- GeForce RTX 2060
- GeForce RTX 2060 Super
- GeForce RTX 2070
- GeForce RTX 2070 Super
- GeForce RTX 2080
- GeForce RTX 2080 Super
- GeForce RTX 2080 Ti
- Nvidia Titan RTX
- GeForce RTX 3060
- GeForce RTX 3060 Ti
- GeForce RTX 3070
- GeForce RTX 3070 Ti
- GeForce RTX 3080
- GeForce RTX 3080 Ti
- GeForce RTX 3090
Not all of Nvidia’s graphics cards provide the same performance increases, however, with the RTX 3000 series often outperforming RTX 2000 designated GPUs. This is because the newer graphics cards house second-generation Tensor Cores, offering a greater per-core performance.
What games support DLSS?
It’s up to developers to implement DLSS, meaning not all games support it, but Nvidia has made a concerted effort to make the process as straightforward as possible.
Currently, there are three ways for developers to introduce DLSS into their games, including natively from within Unity, downloading the Unreal Engine plugin, or grabbing the newly available SDK. Support for DLSS is growing all the time, with new games getting the feature every month – a number we expect to grow exponentially with how accessible it now is.
Here is the long list of games that support DLSS so far:
- Amid Evil
- Anthem
- Aron’s Adventure
- Back 4 Blood
- Battlefield V
- Battlefield 2042
- Bright Memory
- Call of Duty: Black Ops Cold War
- Call of Duty: Modern Warfare
- Call of Duty: Warzone
- Chernobylite
- Control
- CRSED: F.O.A.D. (Formerly Cuisine Royale)
- Crysis Remastered
- Cyberpunk 2077
- Death Stranding
- Deliver Us the Moon
- Doom Eternal
- Dota 2
- Dying: 1983
- Edge of Eternity
- Enlisted
- Escape From Naraka
- Everspace 2
- Far Cry 6
- F1 2020
- F1 2021
- Final Fantasy XV
- Fortnite
- Ghostrunner
- Gu Jian Qi Tan Online
- Icarus
- Into the Radius VR
- Iron Conflict
- Justice
- LEGO Builder’s Journey
- Marvel’s Avengers
- MechWarrior 5: Mercenaries
- Metro Exodus
- Metro Exodus PC Enhanced Edition
- Minecraft With RTX For Windows 10
- Monster Hunter: World
- Moonlight Blade
- Mortal Shell
- Mount & Blade II: Bannerlord
- Necromunda: Hired Gun
- Nine to Five
- Naraka: Bladepoint
- No Man’s Sky
- Nioh 2 – The Complete Edition
- Outriders
- Pumpkin Jack
- Rainbow Six Siege
- Ready or Not
- Red Dead Redemption 2
- Redout: Space Assault
- Rust
- Scavengers
- Shadow of the Tomb Raider
- Supraland
- System Shock
- The Ascent
- The Fabled Woods
- The Medium
- The Persistence
- War Thunder
- Watch Dogs: Legion
- Wolfenstein: Youngblood
- Wrench
- Xuan-Yuan Sword VII
With Nvidia’s investment into ARM and rumours swirling about the Nintendo Switch Pro featuring a new SoC, we might eventually see DLSS appear outside of gaming PCs. For now, though, Nintendo is sticking with the current Tegra in the Switch OLED, meaning it’s only accessible on PCs rocking an RTX graphics card.
{“schema”:{“page”:{“content”:{“headline”:”Nvidia DLSS graphics explained”,”type”:”hardware”,”category”:”gaming-hardware”},”user”:{“loginstatus”:false},”game”:{“publisher”:””,”genre”:null,”title”:”Gaming hardware”,”genres”:null}}}}